-
Metal slag appears as a byproduct of smelting cast iron in converter furnaces for steel production. Phosphorous impurities in the iron react with the furnace lining, float above the molten iron, and then form a dark porous mass. Slag acts as an alkaline fertilizer suitable for acidic or neutral soils, and its effectiveness is limited to these types of soils.
-
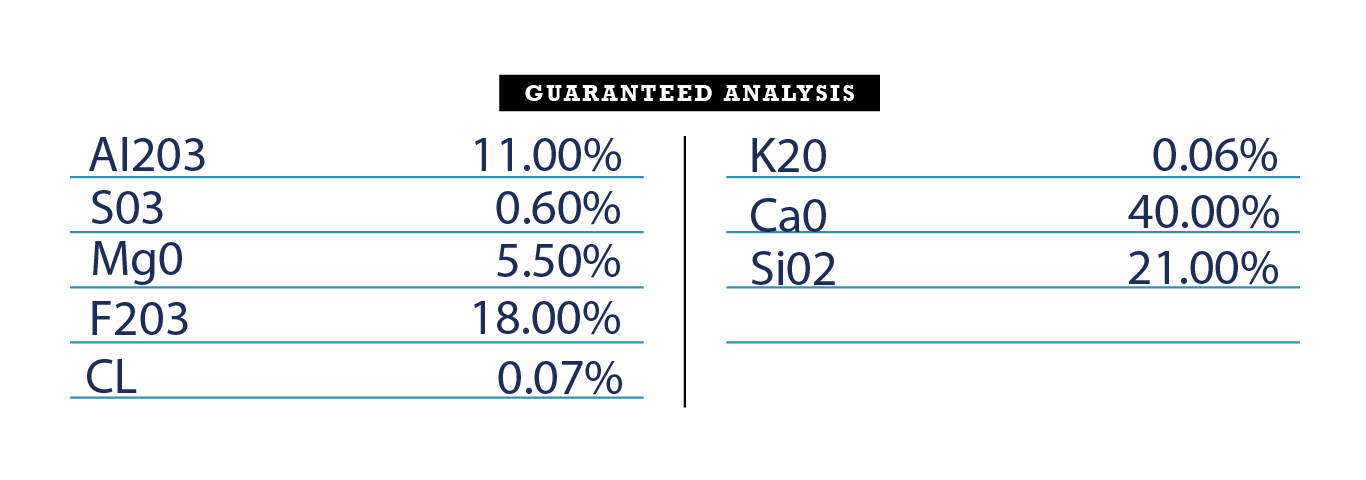
The composition of slag varies, and it is also known as "Thomas phosphate" after one of the innovators of furnace lining. Generally, the fertilizer contains 10 to 25% pentavalent phosphorus oxide in the form of calcium quadruple phosphate, which dissolves in water with difficulty and slowly, along with oxides of magnesium, silicon, and iron.
-
Slag is considered a crucial element in metal extraction through thermal processes, performing chemical and physical tasks ranging from aggregating metallic impurities and oxides to absorbing impurities in metal refining stages. Slag also aids in protecting molten metals from oxidation and reducing heat loss. In electric arc furnaces, slag is used as a means of thermal resistance.
Uses of slag
The slag can be crushed and used as a construction material in road construction and concrete production. Thanks to its durable and stable nature, it is considered a valuable material for creating strong and long-lasting structures
Ground granulated blast furnace slag from high furnaces is considered an auxiliary element in cement mixtures, enhancing the durability and workability of concrete. Therefore, it is an integral part of the cement manufacturing process.
Slag can be used as a soil amendment to increase its fertility and improve its structure. Its mineral composition provides essential nutrients for plants, making it a sustainable choice for agricultural uses.
Due to its strength and effective abrasiveness, slag is an excellent choice for surface preparation and cleaning in industrial areas. It efficiently cleans surfaces from paints, rust, and various types of deposits.
When processed appropriately, slag can be used in the production of lightweight concrete blocks. These blocks are characterized by improved insulation properties and lighter weight compared to traditional concrete blocks.

 AR
AR