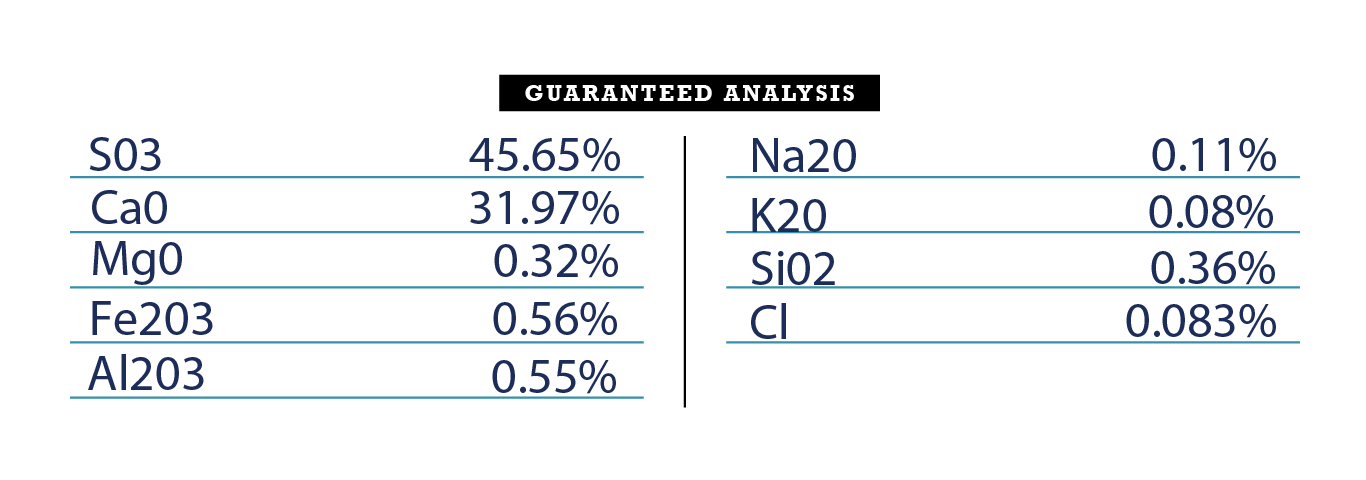
-
Gypsum, also known as calcium sulfate dihydrate, is a natural mineral found in sedimentary rock layers worldwide. It forms from the evaporation and replenishment of water containing calcium and sulfates.
-
White or gray in color, gypsum can be ground into a fine powder and heated until most of the moisture is removed—a process known as calcination. Adding water to this powder results in a pliable material that can be molded into shape or cast and hardens to maintain that form. Alternatively, the material can be added to other substances to bind them together.
-
Due to its binding capabilities, gypsum is a fundamental component in some toothpaste formulations. It is also used as plaster for making surgical molds, as an additive in various foods such as canned vegetables, ice cream, and tofu, and as an amendment and conditioner for agricultural applications.
Uses of Gypsum
Gypsum in its natural state is often found with layers of limestone. It's mostly extracted from its natural state through surface mining. To obtain gypsum ore that can be sold for its various uses, it is crushed to size using DDC-Sizers, Feeder-Breakers, Hammermill Crush, Jaw Crush, Roll Crushers, and stored awaiting further processing.
Gypsum is widely used for sedimentation in ponds. It acts as a coagulant compound, aiding in clarifying pond water by removing suspended particles and sediments. This is particularly beneficial in aquaculture, where clean water is essential for the health and visibility of aquatic species.
Gypsum is a key element in manufacturing drywall, also known as gypsum board or plasterboard, providing fire resistance, sound insulation, and ease of installation. These features make gypsum-based products a preferred choice for building and renovating homes and commercial buildings.
In sports, gypsum is used to bind the clay layer on tennis courts. It helps maintain the moisture of the clay, providing a stable and consistent playing surface. These applications are essential for maintaining the quality and playability of clay tennis courts.
In road and highway construction, gypsum is used to improve the structure and stability of the soil. It helps reduce soil erosion and enhances the longevity and durability of road surfaces, making it a valuable material in infrastructure projects.

 AR
AR