-
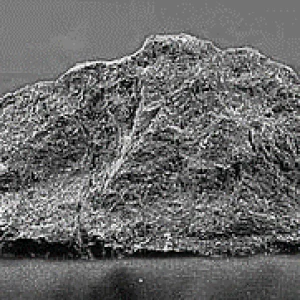
Basalt, a volcanic igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of lava, is known for its extreme hardness, with its name derived from Latin meaning "very hard stone". This black rock, rich in magnesium oxide and calcium and poor in light-colored silicate minerals, is found on Earth as well as on the moon and Mars. It is widely used in industry as construction materials and thermal insulators.
-
Basalt primarily consists of magnesium oxide (MgO) and calcium oxide (CaO), with a very low percentage of silicon dioxide (SiO2), usually less than 50 percent. It also contains some iron oxide (FeO) and aluminum oxide (Al2O3), which give it a dark color, typically appearing in shades of black and green. Sometimes, red or orange colors may appear in basalt due to the presence of iron compounds oxidizing. Basalt forms as an igneous rock from the cooling and crystallization of magma, which usually consists of dark rocks such as peridotite and pyroxene-rich rocks. Some light-colored basalts form when basaltic magma contains a higher-than-usual amount of calcium or sodium-rich minerals.
-
Basalt is primarily used in construction projects such as bricks, tiles, and building foundations, along with sculpting and constructing stone walls for thermal insulation and building railway tracks.
Uses of Basalt
Basalt is extensively used in road construction due to its strength and high resistance to pressure and damage. This durability is derived from its interlocking crystalline structure, providing a sturdy foundation for roads. Additionally, it contributes to the longevity of roads by resisting corrosion and providing a rough surface that enhances vehicle stability.
Basalt is used in both architectural and decorative fields, either for practical purposes or for ornamental purposes. It is preferred for manufacturing tiles, large stones for paving, and pavements to enhance the aesthetic appearance of buildings and outdoor spaces. The natural color spectrum of basalt, ranging from dark gray to black, adds an elegant and modern character to the buildings.
Basalt powder is used as an aggregate material in construction projects, such as forming concrete for buildings and walkways, and as part of asphalt components in roads and highways. Its strength contributes to ensuring the structural safety of concrete, while its insulating properties help reduce energy consumption in buildings.
Basalt fibers, produced by melting rocks and converting them into thin threads, are used in various industries due to their ability to resist heat and chemicals. These fibers are used in the manufacturing of fire-resistant fabrics, automotive components, as well as reinforcing composite materials used in the construction industry.
Basalt can be ground into a fine powder and used as a soil amendment. Its mineral content, such as iron, calcium, and magnesium, supports plant growth, making it a valuable resource for improving depleted soil. Using basalt in this way promotes sustainable agriculture by restoring soil fertility without the use of chemicals.

 AR
AR